Click on each section title below to explore the opportunity in detail.
Core Protein has executed the Master License Agreement with Unibio Plc. and will be the exclusive producer of Uniprotein® in the United States.
- Converting Methane or Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) into Protein
- Decoupling protein production from fishing & farming
CoreProtein® Production
Climate Smart Food Production
- Sustainable production (neutral; no waste; no pesticide or herbicide use)
- Reduced dependency on non-sustainable protein sources (oceans, arable land)
- More efficient use of natural resources (natural gas, land and clean water)
- Additional benefits (turning “fuel into food”; less nitrate in animal excrement
Climate Food Safety and Health
- Industrially produced through an (accelerated) process commonly occurring in nature: and therefore, consistent supply and product quality
- High storage stability
- Good binding power related to (compound feed) pellet production
- Regular supplies at fixed prices (compare: fishmeal, soy)
- Sterile, infection free, non-toxic, non-GMO, non-polluted source
- High protein content (70%+); includes all essential amino acids
- Positive immune effect: healthier growth patterns & less medication needed for animals fed with our protein (cleaner food chain)
- No negative side effects of consumption (compare: soy protein)
The Technology
- Unibio’s technology converts methane into a highly-concentrated Single Cell Protein (“SCP”).
- Is a patented Vertical U-loop® fermentation technology; it achieves productivity yields with the bacterium Methylococcus Capsulatus that allow profitable large scale commercial production
The Protein Products
- UniProtein® is approved in the European Union for use as a component in compound animal feed.
- This Protein is considered to be safe when used as a processing aid in the production of food.
- Because of a strong demand for new sustainable protein sources and the potential cost and performance savings, our protein can easily substitute current more expensive commercial sources of protein in animal feeds. In 2013, over 963 million tons of compound animal feed were produced. The animal feed industry (worth approximately $550 billion in 2015) is our main target market.
- Other applications currently researched by are food-grade (for human) and medicinal-grade proteins.
Protein is an increasingly scarce, though essential nutrient, the production of which is increasingly fraught with environmental issues. Unibio has developed a technology that disrupts this traditional protein value chain while mitigating the traditional challenges.
Animal Protein
- Animal proteins contain all the essential amino acids
- Human diet: meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products
- Livestock/ fish diet: animal by-product meal, fish meal
- Production issues: land use, overfishing, impact on environment
Plant Protein
- No single source contains all of the essential amino acids
- Human diet: legumes, cereals, beans, pulses, grains, nuts, seeds, soya products
- Livestock/fish diet: soybean meal, oil meal crops, legumes, by-products
- Production issues: land use, impact on environment
Microbial Protein (SCP)
- Protein extracted from bacteria through a fermentation process creates Single Cell Protein (SCP)
- No competition with any human food sources
- Can be modified by varying the amino acid composition (but is still non-GMO)
- Production: low land requirement, ecologically beneficial, consistent quality (independent of seasonal and climatic variations)
The production of UniProtein has great benefits for the environment, consumers & producers.
Climate-Smart Food Production
- Sustainable production (CO2 neutral; no waste; no pesticide or herbicide use)
- Reduced dependency on non-sustainable protein sources (oceans, arable land)
- More efficient use of natural resources (natural gas, land and clean water)
- Additional benefits (turning “fuel into food”; less nitrate in animal excrement)
Food Safety & Health
- Industrially produced through an accelerated process commonly occurring in nature.
- Consistent supply and product quality with high storage stability
- Good binding power related to (compound feed) pellet production
- Regular supplies with low price volatility (compared to fishmeal, soy)
- Sterile, infection free, non-toxic, non-GMO, non-polluted source
- High protein content (70%+) includes all essential amino acids
- Positive immune effect: healthier growth patterns & less medication needed for animals fed with UniProtein (cleaner food chain)
- No negative side effects of consumption (compared to soy protein)
Conversion of methane (CH₄) to biomass (”protein”) occurs in nature.
Step 1: Natural gas (methane) occurrence
- Leaves and dead fish fall to the lake floor
- Over time the material decomposes, and a natural gas, high in methane, is produced
Step 2: Methane is eaten by bacteria
- The methane is released into the water and passes through a certain level of water containing minerals and oxygen
- The bacteria, Methylococcus capsulatus, then eat the methane, minerals and oxygen, thus evolving in size and number and becoming rich in protein
Step 3: Bacteria become protein-rich
- Ultimately, the fish and other animals in the lake will eat these bacteria as a source of protein
- The technology provided by Unibio imitates this environment
- By removing liquid, the bacteria turns into biomass
Striving to meet the needs of 10 billion people by 2050
The world needs sustainable solutions to the large scale food challenges of the 21st century
- 10 billion people by 2050
- More and more people = increased demand for protein
Protein production is increasingly challenging
- Diminishing fish stocks
- Scarcity of fresh water
- Cropland limitations
Unibio’s technology can provide protein at a very large scale
- Unibio completely decouples protein production from agriculture and fishing
- Unibio offers a unique alternative to existing sources of protein by the use of an abundant raw material
- Unibio’s technology can provide protein at a very large scale to address global needs
UniProtein® – superior product performance and appealing product characteristics
- Protein-rich biomass (≈70% protein)
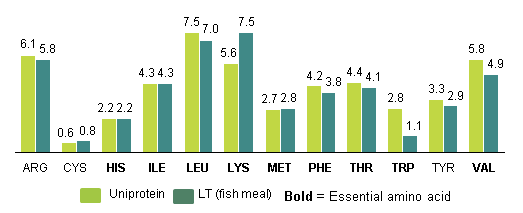
- Better amino acid composition than fishmeal
- Can be used as a direct supplement in animal feed compounds
Tested and Approved in the European Union for use as a component in compound animal feed (EU Commission Regulation 68/2013, section 12.1.2)
Wide range of potential customers for UniProtein®
Already approved as feed for salmon, calves, pigs and chickens with very positive results in terms of acceptance and growth rates.
Potential future applications as an additive for human diet and long-life animal feed
Low Land Footprint
- Relative to soy production, UniProtein® uses 1/25,000th of the land.
- Consequently, UniProtein® holds the potential to significantly improve arable land use across the world.
Oceanic Effect
- Fishmeal is currently produced from either farmed or wild caught fish and puts unsustainable pressure on oceanic ecosystems.
- UniProtein® is almost identical to fishmeal in terms of its protein content and amino acid profile therefore it holds the potential to significantly reduce the pressure on overfishing.
Water Usage
- Relative to soy production, UniProtein® uses 1/300th of the water.
- Most of the water used is recycled in the U-loop fermenter to reduce its consumption.
- Reducing water usage in feed production is a critical sustainability factor.
CO2 Effect
- The CO2 profile of UniProtein® varies depending the source of the methane.
- When bio-methane or flare gas is captured and utilized, production of UniProtein® leads to actual GHG reduction.
- UniProtein® provides additional positive CO2 impacts.
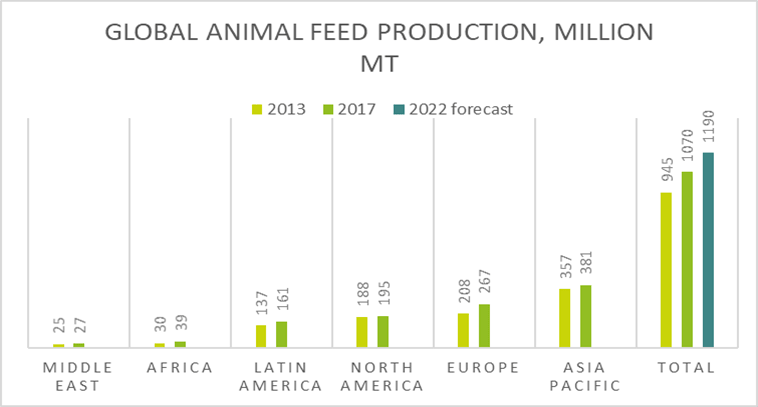
Growth in animal feed production should be viewed in the light of increasing scarcity of raw materials.
- In 2017 approximately 300 million tons of protein was consumed as animal feed
- CAGR is expected to be more than 2% for the foreseeable future
- Total animal feed market value is more than $500 billion
- Protein constitutes 30% of this value – approximately $150 billion